-->
Many products flow from the mining and processing of ores containing molybdenite (MoS2), including:
1. Chemical Mo products
Used in catalysts, polymer compounding, corrosion inhibitors, and high-performance lubricant formulations, these include pure molybdic oxide and molybdates, and lubricant grade MoS2.
2. Meltstock products
Used as alloy additions to iron, steel, nickel, and titanium alloys, these include technical Mo oxide, ferromolybdenum, and Mo metal pellets.
3. Mo metal products
These include powder, Mo metal and Mo-base alloy mill products, and products fabricated from them such as LCD Screen, Air Plane Avionics etc.
Most of molybdenum used in stainless steel industry. Molybdenum is a ferrite former, so corrosion resistivity is very high.
Before used, concentrate from flotation should be freed of sulfide which is done by roasting:
MoS2 + 3 ½ O2 = MoO3 + 2 SO2
MoS2 + 3 O2 = MoO2 + 2 SO2
Reaction in roasting occurs with heat evolution, process is carried out at 590-620 oC in Multiple hearth furnace.
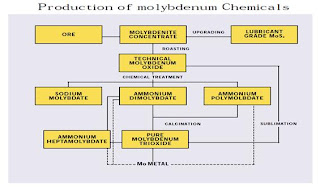
Figure 4.
-->Production of Molybdenum Products

Figure 5. Roasting Plant
The next process for Chemical Mo dan Mo metal can be shown in Figure 6.
Ferromolybdenum (FeMo) producted by aluminothermic reaction:
MoO2 + FeO + 2 Al = FeMo + Al2O3
This is a spontaneous reaction until 2000 oC with KMnO4 as an ignition, phase diagram of Fe-Mo can be shown in figure 7.
Figure 7. Phase Diagram of Fe-Mo
-->
Ferromolybdenum (FeMo)
FeMo can be used in any melting or refining unit to produce Mo-containing steel or cast iron. It is frequently used as ladle addition to achieve accurate final adjustment of composition. In steels with low Mo content (usually no more than 0.2% Mo) like High Strength Low Alloy (HSLA) steel, all of the Mo is added as FeMo.
FeMo typically contains 65 – 75% Mo and a maximum of 0.5% Cu.
The product is produced in size ranges between:
0 and 10 mm, and 10 mm on the low side and several maximum size limits between 20 and 100 mm. It is available as powder for special applications like welding electrodes.

Figure 8. Ferromolybdenum
 Figure 9. Ferromolybdenum Plant
Figure 9. Ferromolybdenum Plant
Packaging is normally in steel drums or big bags.
Product standards include:
ASTM A132-04 Standard Specification for Ferromolybdenum
DIN 17561, 2004-02, Ferromolybdän





1 comment:
Hallo Mas Andik,
didukung mas tujuan mulianya untuk mencerdaskan anak bangsa khususnya ilmu metallurgi,..
saya juga coba bikin tentang material http://material-review.blogspot.com
boleh coba beri saran untuk perbaikan..thanks
Post a Comment